Defining Metrorrhagia
Metrorrhagia is unusual bleeding between cycles of menstruation. Metrorrhagia (irregular bleeding) is among the most common menstrual irregularities identified. This condition is also known as intermenstrual bleeding, breakthrough bleeding, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, breakthrough menstrual bleeding, spotting between menses, inter- menstrual bleeding, spotting between periods. Even though this kind of bleeding comes from the womb, just like it does during a period, it is not recognized as a component of the menstrual cycle. As much as one third of women will have uterine bleeding that is unusual at some point in their lives, with irregularities most common around menarche and perimenopause. The average rate of abnormal bleeding from the uterus among reproductive-aged women globally is believed to be around 3% to 30%, with more episodes occurring around menarche and perimenopause
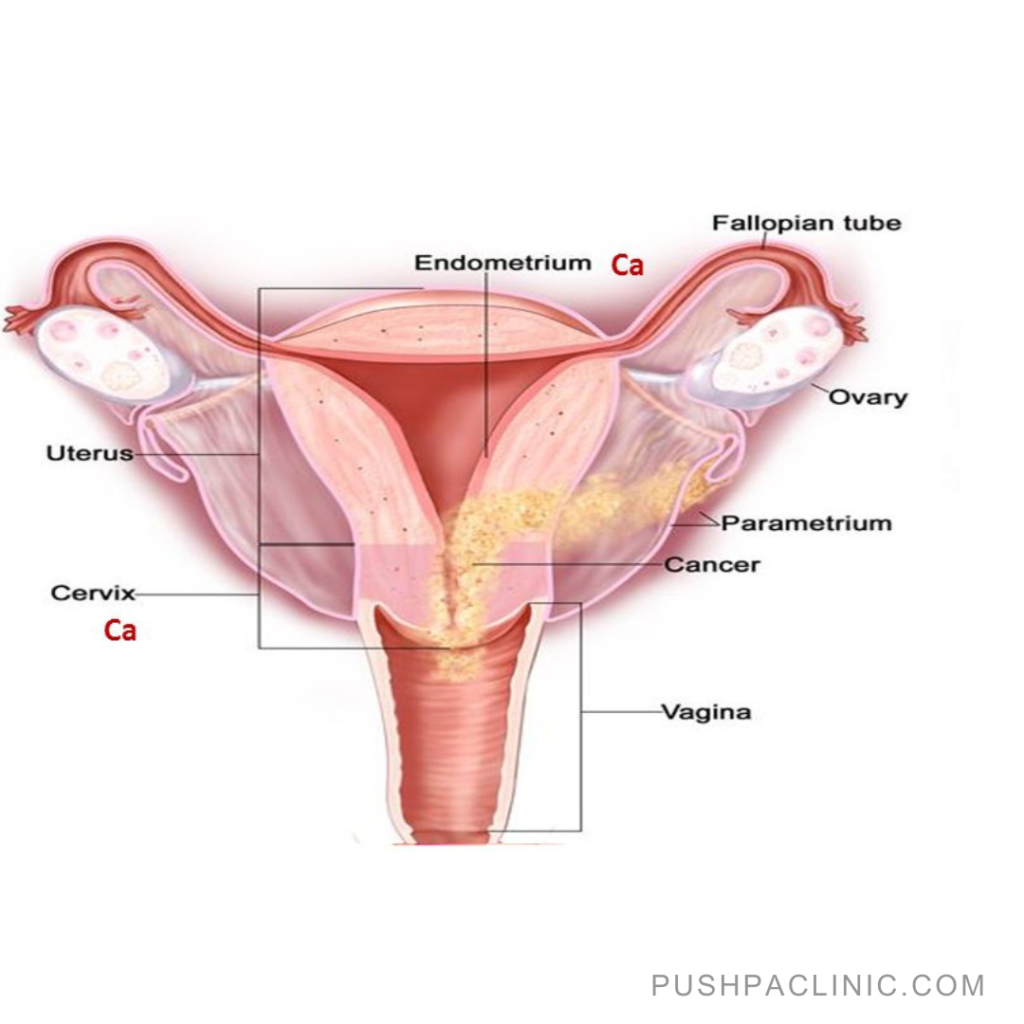
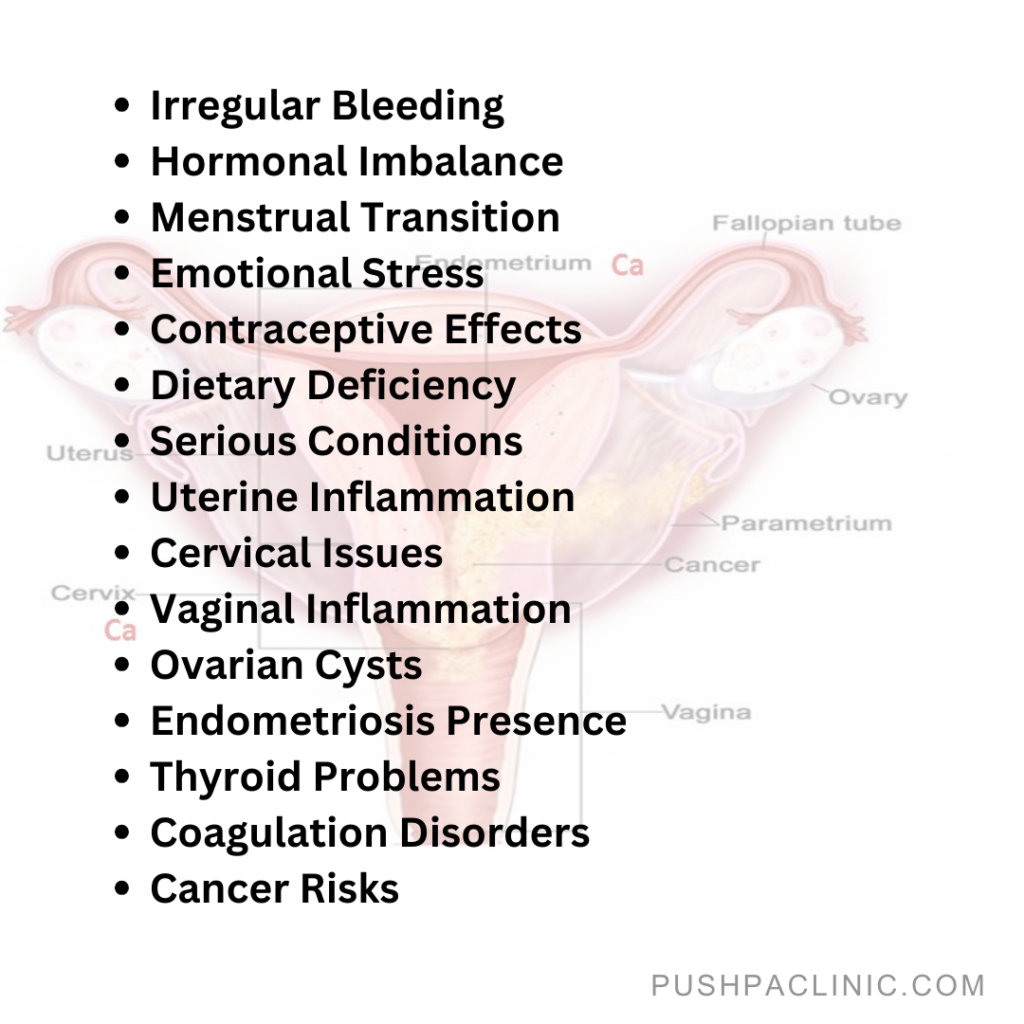
Causes of Metrorrhagia
Uterine bleeding that is irregular that is not caused by menstruation, typically in females who do not have regular periods. The inconsistent and unexpected bleeding is frequently caused by a malfunctioning endometrium. Metrorrhagia can be caused by a variety of factors, including an imbalance in hormones, irregular development, pregnancy difficulties, and infection. If you develop metrorrhagia, you should consult your doctor right away. Metrorrhagia remedies vary based on the underlying reason.
The detailed reasons are listed below:
- First or last period: It is common for the menstrual cycles to be irregular and for vaginal bleeding to occur at different times when the cycles are first starting or are about to cease (menopause).
- Stress: Emotional and other sorts of stress can significantly alter your menstruation and produce abnormal uterine flow.
- Contraception and medication: Unexpected vaginal bleeding may occur as a result of birth control pills or other medications.
- Poor diet: When people are underweight, their menstrual cycles often halt completely, or they experience intermenstrual bleeding. This is primarily due to a lack of specific dietary groups and bad eating habits in general.
- Other serious health conditions: The condition could be endometritis, or uterine inflammation, cervicitis (cervical inflammation), vaginitis (vaginal inflammation), inflammatory pelvic conditions and sexually transmitted infections, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, thyroid issues, coagulation problems, disorders Related to Leukemia, PCOS, problems with the uterus (size, location, etc.,) and/or cervical, vaginal, ovarian, vulvar, endometrial, uterine, and fallopian tube cancer.
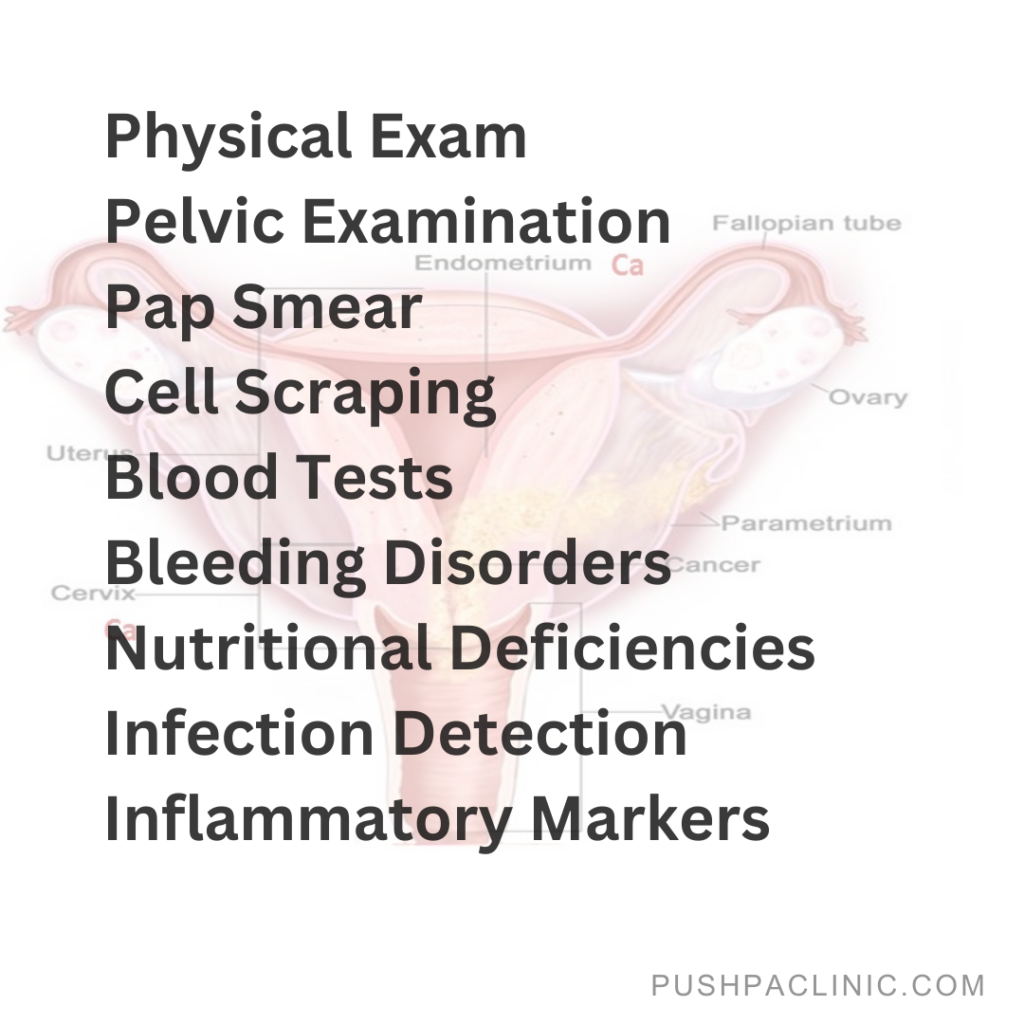
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes the following check-ups:
- Physical Exam: A pelvic exam (which involves inserting a speculum into your vagina and spreading the vaginal walls) may also be performed. A Pap smear involves scraping cells from the cervix with a lengthy swab. The sample will next be examined for any irregularities.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are used to detect bleeding disorders, nutritional deficiencies, infections, inflammatory markers, along with additional results.
Treatment
The possibilities for therapy include the following choices:
Lifestyle changes: In certain circumstances, the condition is only transitory and can be improved by changing your lifestyle. For example, if body weight is an issue, one can engage in physical exercise to gain or lose weight, depending on their needs.
Hormone Therapy: Certain types of hormone therapy, particularly those containing progestin, can be used to address abnormal bleeding. These may include birth control pills, IUDs, estrogen patches, and other choices.
Addressing Underlying Health Conditions: If metrorrhagia is caused by another health issue, it must be appropriately evaluated and treated.
Hormone Therapy: Certain types of hormone therapy, particularly those containing progestin, can be used to address abnormal bleeding. These may include birth control pills, IUDs, estrogen patches, and other choices.

